Understanding
The probability of a compound event can be found by listing the outcomes for one event followed by the other, creating a probability tree, or by using the product rule for independent events.
What to look for
Students should understand when it is appropriate to multiply the probabilities of individual outcomes in order to determine the probability of a compound event.
Sample Assessment
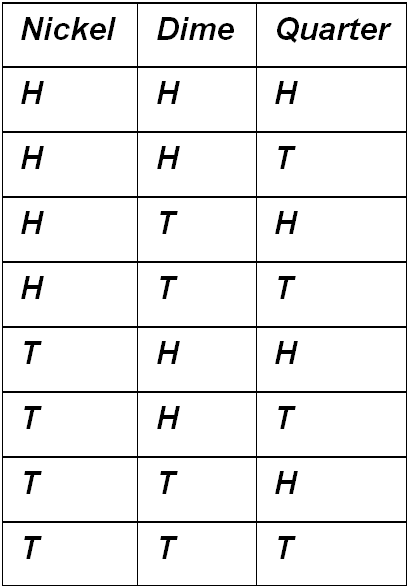
A nickel, a dime, and a quarter are flipped at the same time. Each coin can land either heads up (H) or tails up (T). List all the different possible outcomes for this event in the chart below. The list has been started for you.

Answer: